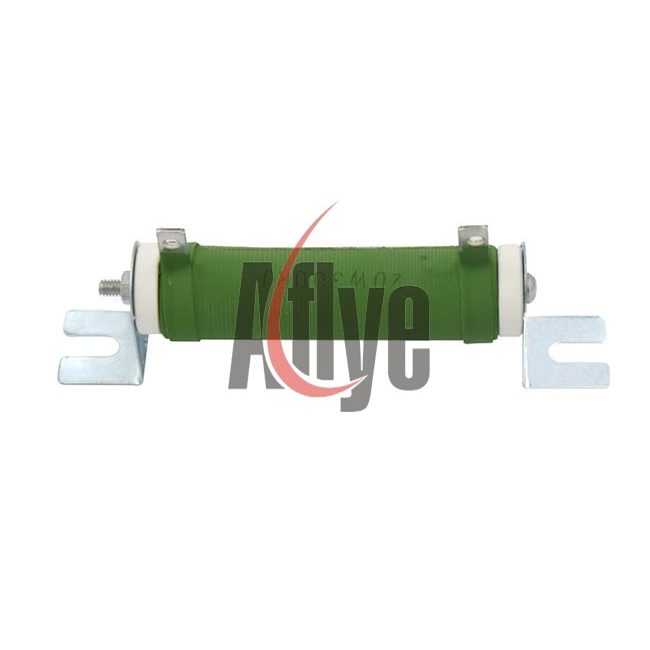
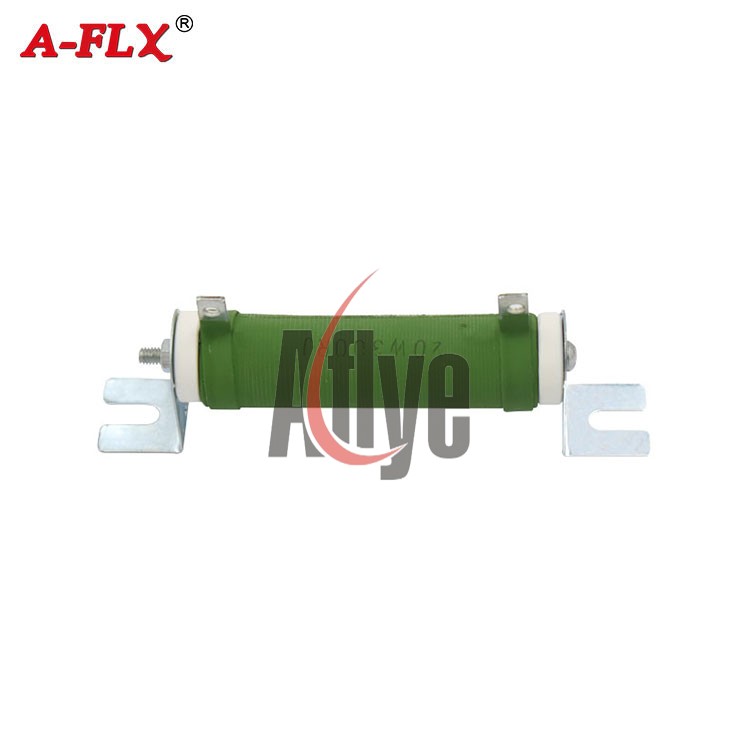
20W 300ΩJ Elevator Adjustable Resistor
Elevator Adjustable Resistors Principle
The principle of adjustable resistors in elevators mainly involves controlling the current by adjusting the resistance value, which in turn affects the elevator’s operation.
The adjustable resistor in an elevator, also known as a braking resistor, is primarily used for braking when the DC bus voltage of the frequency converter is too high. When the elevator descends, the weight of the car causes the motor to be dragged, putting the motor in a generating state, which leads to an increase in the bus voltage of the frequency converter. To prevent the voltage from becoming too high and damaging the equipment, the braking resistor consumes the regenerative energy of the motor (in the form of heat) to reduce the bus voltage, thereby protecting the elevator equipment from damage. The resistance value and power capacity of the braking resistor are two important parameters that work together to ensure the safe operation of the elevator.
Additionally, an adjustable resistor itself is an electronic component that can have its resistance value adjusted within a certain range, thereby altering the current in the circuit. There are various types of adjustable resistors, including electronic adjustable resistors, ceramic disk adjustable resistors, surface-mount adjustable resistors, and wire-wound adjustable resistors. These different types of adjustable resistors have distinct designs and applications, but their common purpose is to control and regulate the circuit by adjusting the resistance value.
In summary, the braking resistor in an elevator protects the equipment from high voltage damage by consuming the motor’s regenerative energy, while the adjustable resistor precisely controls the current in the circuit by altering its resistance value. Together, these components ensure the safe and efficient operation of the elevator.